Chapter 12. Methane Fermentation (14 pages)
- 1.General provisions
- 1.1.Acidification
- 1.2.Temperature regulation
- 1.3.pH
- 1.4.Safety devices
- 1.5.Gas storage
- 1.6.Gas treatment
- 2.Suspended growths
- 2.1.Analift (mixed digester + settling - thickener tank)
- 2.1.1.Design
- 2.1.2.Applications and performances
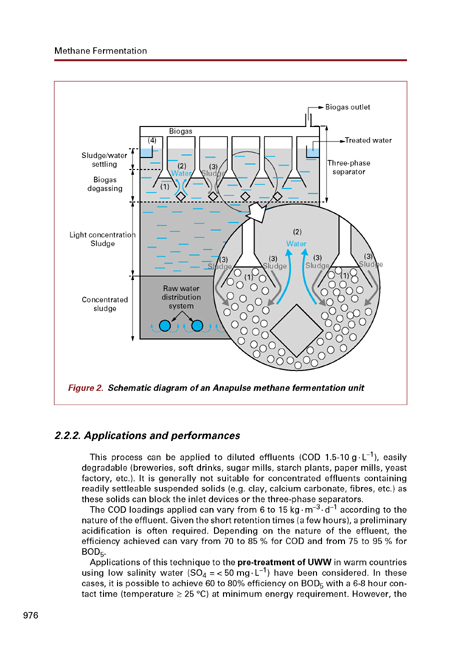
- 2.2.Anapulse (sludge blanket digester)
- 2.2.1.Design
- 2.2.2.Applications and performances
- 3.Attached growths
- 3.1.Anaflux (attached growth in fluidised beds)
- 3.1.1.Design (figure 3)
- 3.1.2.Applications and performances
- 4.Plant start-up and control
- 4.1.Start-up and seeding
- 4.2.Operating parameters
- 4.3.Post-treatment
Introduction
Methane fermentation has been used for more than a century ago in the treatment of urban sludge at wastewater treatment plants. Effectively, this method helps to reduce sludge volatile content and, consequently its mass; methane fermentation process offers additionally sludge homogenisation (15-20 days of mixing in digester), and a sludge dewatering equalisation, and all this for a minimum energy requirement: the energy generated by biogas production offset the energy required for heating and mixing in the digester.
These features of methane fermentation, mainly its BOD reduction at low energy requirement and at minimum sludge production result in the extension of its application to the treatment of industrial wastewater (IWW) containing high levels of dissolved organics. Over the past 20 years, various technologies have been developed by Degrémont, including techniques by suspended growth or by attached growth (table 1). These equipments are known as either digesters or methane fermentation units.
This chapter only addresses methane fermentation of the effluents; sludge digestion is discussed in chap. 18 § 4. (liquid sludge stabilisation).